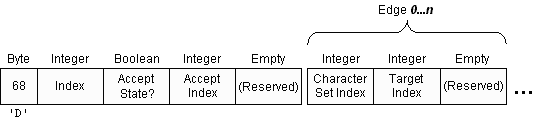

Each record describing a state in the DFA State Table is preceded by a byte field containing the value 68 - the ASCII code for "D". The file will contain one of these records for each state in the table. The Table Count record, which precedes any DFA records, will contain the total number of states.
The record contains information about the state itself: where it is located in the DFA State table and what symbols can be accepted (if any). Following this, there is a series of fields which describe each edge of the states. A DFA state can contain 0 or more edges, or links, to other states in the Table. These are organized in groups of 3 and will constitute the rest of the record.
| Item | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Index | Integer | This parameter holds the index of the DFA state in the DFA State Table. |
| Accept State? | Boolean | Each DFA state can accept one of the grammar's terminal symbols. If the state accepts a terminal symbol, the value will be set to True and the Accept Index parameter will contain the symbol's index. |
| Accept Index | Integer | If the state accepts a terminal symbol, this field will contain the symbol's index in the Symbol Table. Otherwise, the value in this field should be ignored. |
| (Reserved) | Empty | This field is reserved for future use. |
| Edge 0...n | Described below. |
| Value | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Character Set Index | Integer | Each edge contains a series of characters that are used to determine whether the Deterministic Finite Automata will follow it. The actual set of valid characters is not stored in this field, but, rather, an index in the Character Set Table. |
| Target Index | Integer | Each edge is linked to state in the DFA Table. This field contains the index of that state. |
| (Reserved) | Empty | This field is reserved for future use. |